티스토리 뷰
1. 상속의 키워드
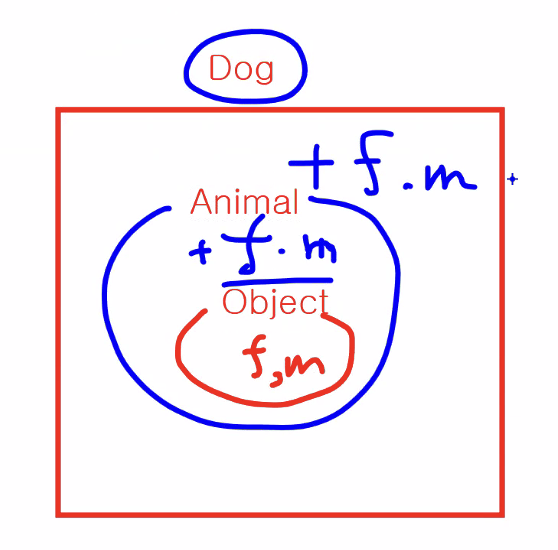
1-1. IS-A
💡 "자식 클래스는 (하나의)부모 클래스이다." 라는 말을 만족(성립)하는 관계를 뜻한다.
클래스 간 상속 관계를 파악하기 위한 키워드
ex) Circle is a Shape
원은 하나의 모양이다.


- Product is a Computer (X)
- Computer is a Product (O) → 자식 : Computer / 부모 : Product
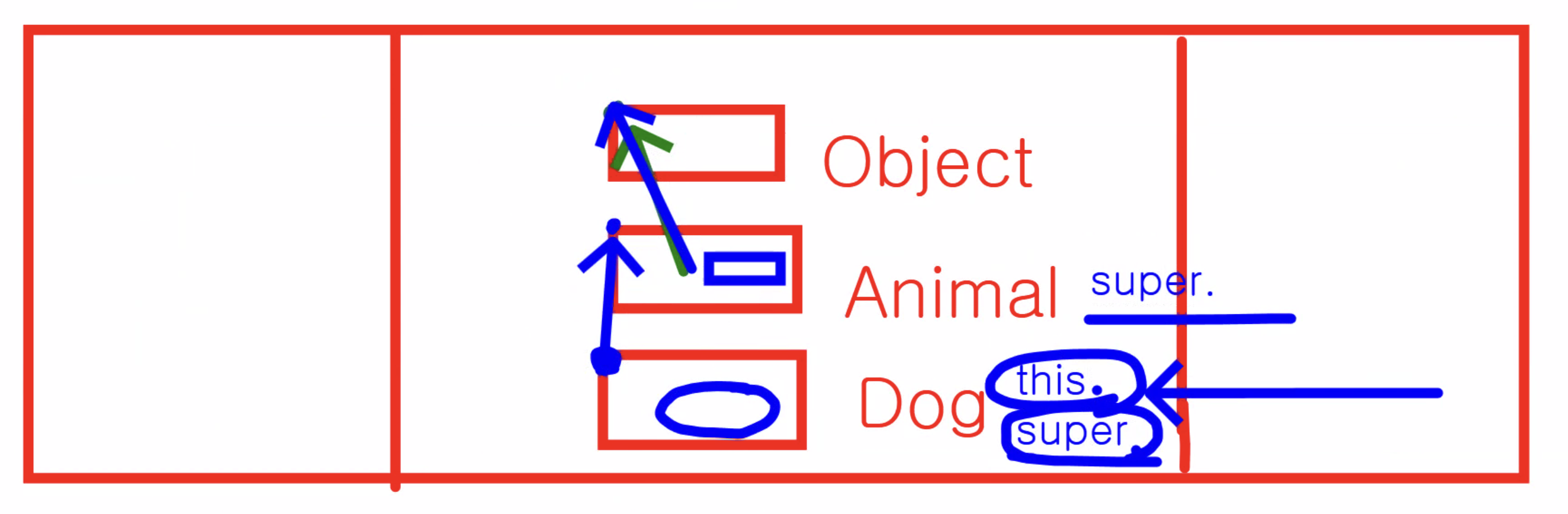
1-2. super와 super()
💡 인스턴스 생성 시 부모 생성자를 호출하여 부모 클래스의 인스턴스도 함께 생성하게 된다.
이 때 생성한 부모 인스턴스의 주소를 보관하는 레퍼런스 변수로 자식 클래스 내의 모든 생성자와 메소드 내에서 묵시적으로 사용할 수 있는 레퍼런스 변수이다.
💡 super()는 부모 생성자를 호출하는 구문
→ 인자와 매개변수의 타입, 갯수, 순서가 일치하는 부모의 생성자를 호출하게 된다.
→ super()는 부모 클래스가 가지는 private 생성자를 제외한 나머지 생성자를 호출할 수 있도록 한 구문.
package com.ohgiraffers.section02.superkeyword;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 수업목표. super. 과 super() 에 대해 이해할 수 있다. */
/* 필기.
* super.: 자식 클래스 타입의 객체가 생성될 때 먼저 생성된 부모 클래스 타입의 객체의 주소값(참조값)을 통해 접근
* super(): 부모로부터 물려받지 못한 생성자를 부모 클래스에 있는 생성자를 활용하기 위해 사용
* */
Product product1 = new Product();
System.out.println(product1); // toString 결과 나온다.
Product product2 = new Product("p01", "플레이데이터", "자바", 1000, new java.util.Date());
System.out.println(product2);
// System.out.println(new java.util.Date().toString());
Computer computer1 = new Computer();
System.out.println(computer1);
Computer computer2 = new Computer("퀄컴 스냅드래곤", 512, 16, "안드로이드");
System.out.println(computer2);
Computer computer3 = new Computer("s-1234", "구글", "픽셀", 1000000, new java.util.Date(), "퀄컴 스냅드래곤", 1024, 32, "윈도우");
System.out.println(computer3);
}
}
// 실행 결과
Product{code='null', brand='null', name='null', price=0, manufacturingDate=null}
Product{code='p01', brand='플레이데이터', name='자바', price=1000, manufacturingDate=Wed Jul 17 19:02:48 KST 2024}
Computer{code=null, brand=null, name=null, price=0, manufacturingDate=nullcpu='null', hdd=0, ram=0, operatingSystem='null'}
Computer{code=null, brand=null, name=null, price=0, manufacturingDate=nullcpu='퀄컴 스냅드래곤', hdd=512, ram=16, operatingSystem='안드로이드'}
Computer{code=s-1234, brand=구글, name=픽셀, price=1000000, manufacturingDate=Wed Jul 17 19:02:48 KST 2024cpu='퀄컴 스냅드래곤', hdd=1024, ram=32, operatingSystem='윈도우'}package com.ohgiraffers.section02.superkeyword;
import java.util.Date;
public class Computer extends Product{
private String cpu;
private int hdd;
private int ram;
private String operatingSystem;
public Computer() {
super();
}
public Computer(String cpu, int hdd, int ram, String operatingSystem) {
super();
this.cpu = cpu;
this.hdd = hdd;
this.ram = ram;
this.operatingSystem = operatingSystem;
}
public Computer(String code, String brand, String name, int price, Date manufacturingDate, String cpu, int hdd, int ram, String operatingSystem) {
super(code, brand, name, price, manufacturingDate); // 부모 걸로 가져와야한다.
// super.setCode(code); // 위처럼 하지 않으면 일일이 가져와야한다.
this.cpu = cpu;
this.hdd = hdd;
this.ram = ram;
this.operatingSystem = operatingSystem;
}
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public void setCpu(String cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public int getHdd() {
return hdd;
}
public void setHdd(int hdd) {
this.hdd = hdd;
}
public int getRam() {
return ram;
}
public void setRam(int ram) {
this.ram = ram;
}
public String getOperatingSystem() {
return operatingSystem;
}
public void setOperatingSystem(String operatingSystem) {
this.operatingSystem = operatingSystem;
}
// /* 이렇게 getBrand를 만들어주고 toString에 그냥 getBrand만 쓰면
// * Computer의 getBrand를 가져옴 */
// public String getBrand() {
// return cpu;
// }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Computer{" +
"code=" + this.getCode() + // 부모거는 우회로 메소드로 불러올 수 있다. 물려받았지만 엄연히 다른 객체이기 때문에!!!
// this. 로도 가능??? 이름이 겹치지 않으면? 어떤 이름?
", brand=" + getBrand() + // 이쪽 super. 은 지워도 된다. getBrand() 만들지 않았으면
", name=" + super.getName() +
", price=" + super.getPrice() +
", manufacturingDate=" + super.getManufacturingDate() +
"cpu='" + cpu + '\'' +
", hdd=" + hdd +
", ram=" + ram +
", operatingSystem='" + operatingSystem + '\'' +
'}';
// return super.toString() +
// "Computer{" +
// "cpu='" + cpu + '\'' +
// ", hdd=" + hdd +
// ", ram=" + ram +
// ", operatingSystem='" + operatingSystem + '\'' +
// '}';
}
}
package com.ohgiraffers.section02.superkeyword;
import java.util.Date;
public class Product {
private String code;
private String brand;
private String name;
private int price;
private java.util.Date manufacturingDate;
public Product() {
}
public Product(String code, String brand, String name, int price, Date manufacturingDate) {
this.code = code;
this.brand = brand;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.manufacturingDate = manufacturingDate;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Date getManufacturingDate() {
return manufacturingDate;
}
public void setManufacturingDate(Date manufacturingDate) {
this.manufacturingDate = manufacturingDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"code='" + code + '\'' +
", brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", manufacturingDate=" + manufacturingDate +
'}';
}
}
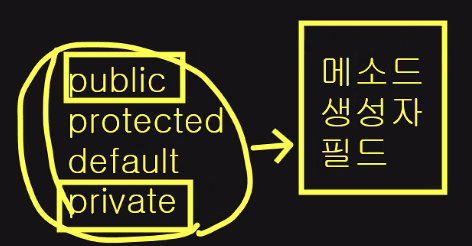
- class 는 public or default
- 필드는 public or private
- 나머지는 모두 다 사용 가능
'한화시스템 > 백엔드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BE] JAVA_다형성 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
|---|---|
| [BE] JAVA_상속_오버라이딩 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| [BE] JAVA_상속_개요 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| [BE] JAVA_클래스와 객체_uses 예제 (0) | 2024.07.16 |
| [BE] JAVA_클래스와 객체_객체 배열 (0) | 2024.07.16 |
